Date
September 23, 2024
Written By
Team DarDoc
Category
Guide
In the pursuit of achieving a brighter, more even skin tone, many individuals are turning to nutritional solutions that complement their daily skincare routine. While topical treatments often focus on short-term fixes, research suggests that micronutrients—vitamins, minerals and antioxidants—can significantly contribute to skin health and skin whitening from the inside out. In this blog, we’ll explore the science behind how micronutrients help regulate skin pigmentation, and how incorporating them into your daily skincare routine can lead to visible results in skin tone. We’ll also dive into the specific nutrients that show promise for those wondering how to whiten skin naturally and safely.
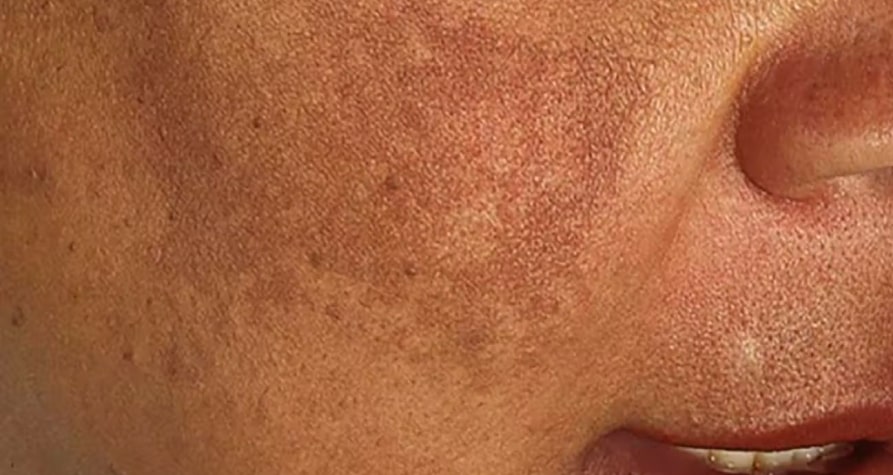
Understanding Skin Pigmentation and How Micronutrients Help
Skin pigmentation is influenced by melanin, the pigment produced by specialized cells called melanocytes. While melanin protects the skin from UV radiation, an excess of melanin, due to sun exposure, hormonal fluctuations, or oxidative stress, can lead to dark spots or an uneven complexion.
For those looking to understand how to whiten skin, it’s important to note that certain micronutrients can regulate melanin production, reduce oxidative stress, and calm inflammation—factors that contribute to skin whitening. The right balance of these nutrients can be an essential part of any daily skincare routine focused on lightening and brightening skin.
Book now
Key Micronutrients for Skin Whitening and Pigmentation Control
1. Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid)
Vitamin C is perhaps the most well-known micronutrient when it comes to skin whitening. It works by inhibiting tyrosinase, the enzyme responsible for melanin production. This makes it a powerhouse for reducing skin pigmentation and brightening the complexion.
In addition, vitamin C supports collagen synthesis, promoting skin renewal and giving the skin a more youthful, radiant appearance. Incorporating vitamin C into both your diet and daily skincare routine—through topical serums and oral supplements—can have a dual action of brightening and improving skin texture. For optimal results, consider pairing vitamin C with other antioxidants to enhance its skin-lightening effects.
2. Glutathione
For those wondering how to whiten skin effectively, glutathione is an increasingly popular option. It’s a potent antioxidant that directly influences melanin production by shifting it from eumelanin (darker pigment) to pheomelanin (lighter pigment). By reducing oxidative stress, glutathione also prevents excess melanin from being produced due to environmental damage.
Studies have shown that glutathione supplementation, whether oral or intravenous, has a measurable effect on skin whitening. In one clinical trial, participants who took glutathione supplements for 12 weeks reported a noticeable reduction in skin pigmentation, making it a go-to nutrient for anyone wanting to brighten their skin tone.
3. Niacinamide (Vitamin B3)
Niacinamide, another key player in skin whitening, functions by inhibiting the transfer of melanin to the skin’s surface cells. This mechanism helps lighten existing pigmentation and prevent further darkening. As a result, niacinamide is frequently included in topical skincare products aimed at reducing hyperpigmentation and brightening the skin.
Studies have shown that topical application of niacinamide can significantly reduce skin pigmentation in as little as eight weeks. In addition, niacinamide helps strengthen the skin’s barrier, making it an excellent addition to any daily skincare routine focused on both brightening and overall skin health.
4. Vitamin E (Tocopherol)
Vitamin E works synergistically with vitamin C to offer enhanced skin whitening benefits. While vitamin E on its own doesn’t lighten the skin, it helps protect the skin from oxidative stress, which can otherwise trigger an increase in melanin production. Vitamin E is also effective in moisturizing and nourishing the skin, making it an essential part of any daily skincare routine focused on maintaining a healthy glow.
By pairing vitamin E with other antioxidants, such as vitamin C and glutathione, you can create a powerful combination that reduces skin pigmentation and promotes a more even, radiant complexion.
5. Zinc
Though not as directly linked to skin whitening as vitamin C or glutathione, zinc plays an important role in controlling skin pigmentation by reducing inflammation and supporting overall skin health. Inflammation often leads to post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, especially in acne-prone skin. Zinc’s ability to regulate sebum production and accelerate skin healing makes it an important nutrient in preventing and treating dark spots.
Including zinc in your daily skincare routine, either through diet or supplements, can help reduce the occurrence of dark spots and keep your complexion clearer and more even toned.
6. L-Cysteine
L-Cysteine, an amino acid, works alongside glutathione in promoting skin whitening. It encourages the production of pheomelanin, the lighter form of melanin, leading to a lighter overall skin tone. L-Cysteine’s antioxidant properties also reduce the oxidative stress that can cause excess pigmentation, making it a key nutrient for those looking to manage skin pigmentation issues.
Several studies have shown that supplementing with L-Cysteine can amplify the skin-lightening effects of glutathione, providing a natural and effective way to achieve a brighter complexion.

Integrating Micronutrients into Your Daily Skincare Routine
When looking at how to whiten skin naturally, it’s important to approach the process holistically. While topical treatments can target skin pigmentation from the surface, micronutrients work from within to regulate melanin production and support overall skin health. Incorporating the right nutrients into your daily skincare routine—both through diet and supplementation—can lead to long-lasting results.
Here are a few ways to incorporate these micronutrients effectively:
Vitamin C and E: Look for serums containing both vitamins C and E for morning application to protect the skin from sun damage and lighten dark spots.
Glutathione and L-Cysteine: Consider oral supplements, especially if you’re looking for a gradual, all-over brightening effect. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting
Niacinamide: Use a niacinamide serum or moisturizer in your daily skincare routine to prevent the transfer of melanin and reduce hyperpigmentation.
Conclusion
The science behind skin whitening is complex, but micronutrients like vitamin C, glutathione, niacinamide, vitamin E, zinc, and L-Cysteine offer promising solutions for managing skin pigmentation. These nutrients work synergistically to regulate melanin production, reduce oxidative stress, and support skin barrier health.
For those searching for effective ways on how to whiten skin, integrating these micronutrients into your skincare routine through IV drips can yield noticeable results over time.
Book a session
Date
September 23, 2024
Written By
Team DarDoc
Category
Guide